Ever heard of Planned Parenthood and wondered what the organisation’s name meant? If you haven’t, it is an American-based nonprofit organisation that informs millions across the globe on reproductive health care and sex education.
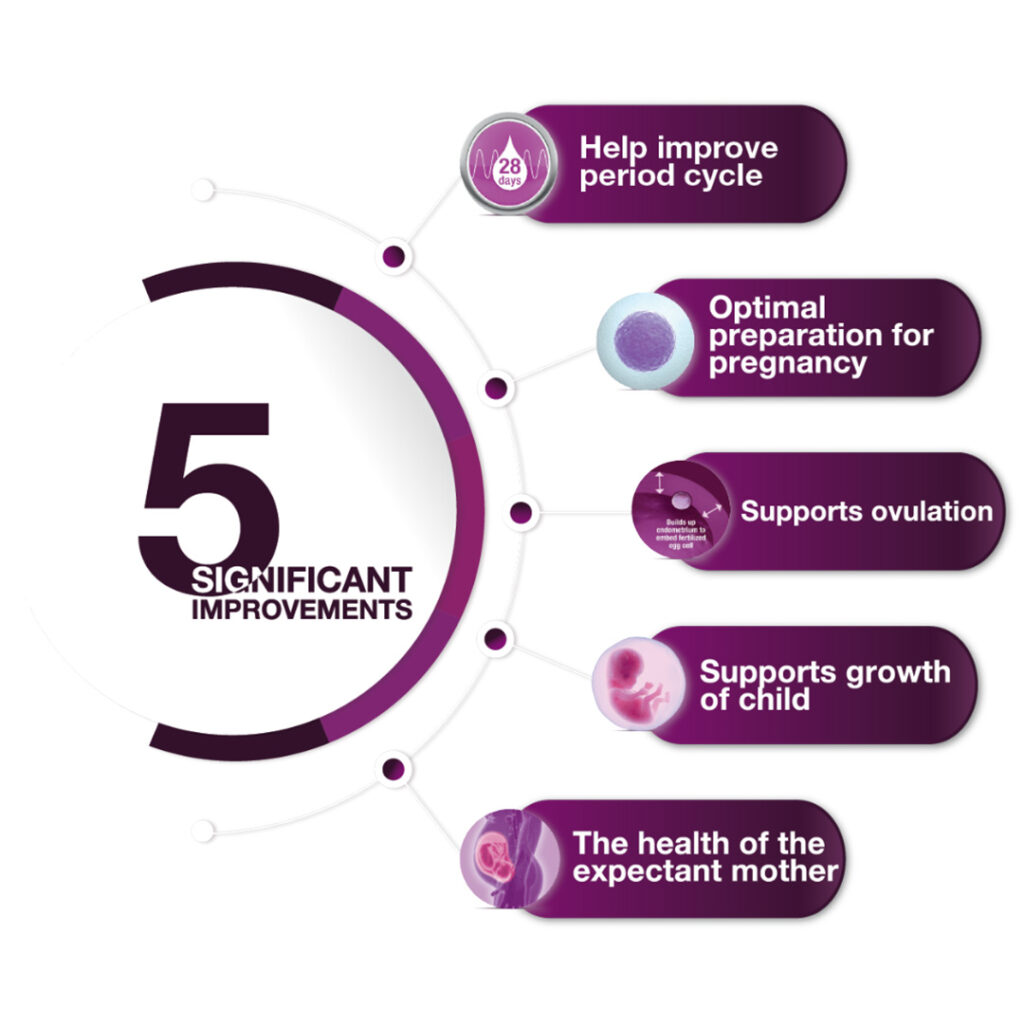
Though the term “planned parenthood” can lead to many things, one of the most important and overlooked aspects of what the organisation does is fertility planning or pre pregnancy planning — a process or set of procedures that help keep you and your future babies safe.
Also known as preconception care, pre pregnancy planning is what helps you discover and solve potential issues that could affect your pregnancy. Despite your family history, it is vital that every woman and their partner go for fertility check ups before planning to have a baby.
What entails a fertility check up?

Think that pre pregnancy planning only involves the carrier i.e. the mother who will be carrying the baby? Think again. It takes both the male and female counterparts to go through a fertility health checkup, an essential part of pre pregnancy planning. This may include ultrasound scans and hormone blood tests for women and a semen quantity and quality analysis for men. In countries like Malaysia, for example, a pre-marriage HIV test is also highly encouraged to reduce the spread of this deadly disease from spouse to spouse or from mother to baby.
Pelvic ultrasound scans, according to John Hopkins Medicine, are the best way to detect abnormalities such as:
- Abnormalities in the anatomic structure of the uterus, including endometrial conditions
- Fibroid tumors, masses, cysts, and other types of tumors within the pelvis
- Presence and position of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and other types of inflammation or infection
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Monitoring of ovarian follicle size for infertility evaluation
- Aspiration of follicular fluid and eggs from ovaries for in vitro fertilisation
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy occurring outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube)
- Monitoring fetal development during pregnancy
- Assessing certain fetal conditions
Here’s what you can expect from a visit to the doctor when it comes to preconception care: your doctor will discuss with you about your own medical history and your family’s medical history, current health issues you may be facing, diet and lifestyle changes, medications that you are on, pregnancy history, and any mental health issues that may affect you should you decide to get pregnant with a baby. You’ll be surprised at just how much it can affect your pregnancy — some doctors may even suggest you book a dentist appointment for a checkup. Why? To prevent health problems for you and your future baby thanks to things like gum disease.
What is a partner’s role in pre pregnancy planning?

Hold up — what is a man’s role in all of this? Thankfully, your partner can play an active role in pre pregnancy planning if you want them to. Getting pregnant and giving birth to a healthy baby is a long and arduous journey that shouldn’t be done alone, hence why it is a partner’s job to make it as easy as possible for you through encouragement and emotional support.
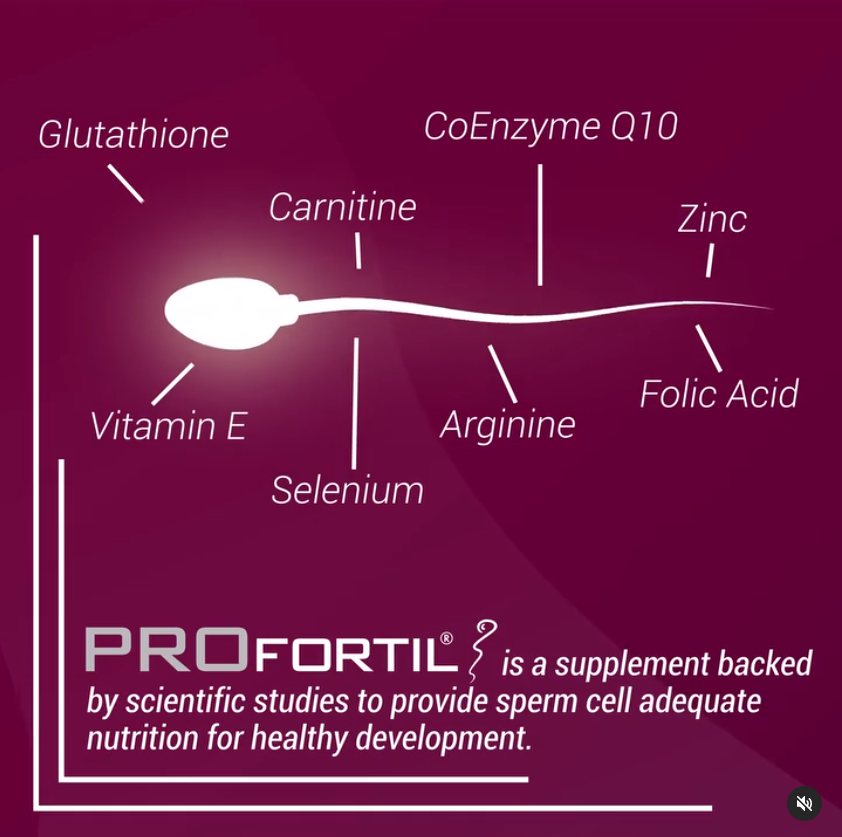
Dietary requirements and lifestyle changes can be hard to keep up with, and this is where the male counterparts can shine. Not only can they take care of your needs and changes, they must make sure that they make an effort on their end too — the diet and lifestyle your partner chooses to adhere to can actually affect sperm count and quality, meaning that you might have issues getting pregnant in the first place.
According to Planned Parenthood, some of the things that can lower a man’s sperm count include but are not limited to:
- smoking or using other kinds of tobacco
- drinking alcohol
- using steroids
- using illegal drugs
- using certain prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines
- being in hot environments frequently such as saunas and steam rooms
- having an unhealthy diet

Does it matter if I go for premarital screenings?
Yes — if you’re worried about having a high risk pregnancy. A high-risk pregnancy, as told by John Hopkins Medicine, is a pregnancy “that involves increased health risks for the pregnant person, foetus or both”. While uncommon, it is best to ensure that you are not part of that demographic through pelvic ultrasound scans, fertility checkups, and regular prenatal screenings at your local hospital.
Some pregnancies can even start off on the right foot but end badly somewhere down the line, which is why regular visits to the doctor are a must to lower your chances of going through a high-risk pregnancy. If you have any of these conditions listed below, it is imperative that you take pre pregnancy planning seriously to avoid complications:
- ○ have high blood pressure, or heart or kidney disease
- ○ have other chronic conditions, like diabetes, lupus, or HIV/AIDS
- ○ have a history of miscarriages, stillbirths, or premature births
- ○ know you’re at risk of having a child with birth defects or a genetic disorder
- ○ have a sexually transmitted infection
- ○ are underweight or overweight
- ○ are older than 35 or younger than 17 years old